Fiber Optic Cable
(a general fiber-optic cable)
Multimode Fiber is cheaper, has a thicker core (which makes it cheaper), but can't go as far and has lower speeds (usually in the 100's of meters)
There always is an exchange of having longer distance for slower speeds, and vice versa.
Datacenters usually use Single Mode fiber which:
- has a smaller core
- is more expensive
- has longer distances (50km or more)
- can go fast
The idea of how these work is that as the light gets sent down the wire, photons move variable distances (some bounce around more). What you'll see is that the light will bleed into the next bit period:
How do we deal with this inter-symbol interference, common in multi-mode fiber? We move to single-mode fiber instead at that point. The smaller glass tube helps reduce the effect of the bouncing, but requires much more materials to make and makes it more expensive.
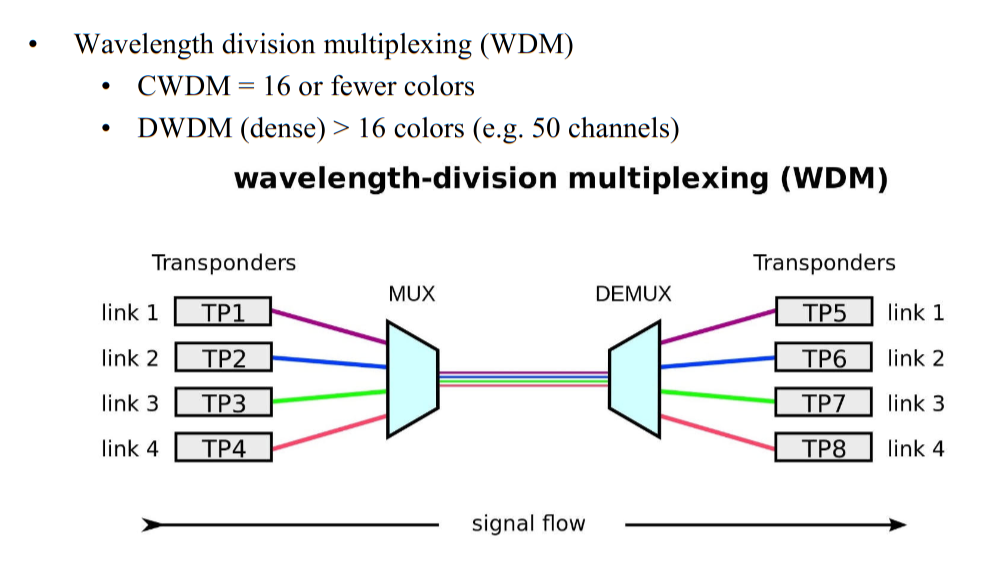
Different wavelengths (colors) of light represent different entry-points, so that one piece of fiber can be shared across the whole wire.